Ignaz Etrich
Ignaz Etrich, also known as "Igo Etrich", was an Austrian pilot and airplane designer, born December 25, 1879 in Horní Staré Město, Trutnov, Bohemia, died February 4, 1967 in Salzburg, Austria.[1]
Etrich was educated at Leipzig, coming into contact with the works of Otto Lilienthal. His main interest was in aviation, the problems of bird flight. With his father, a factory-owner, he built a laboratory for developing airplanes. After the death of Lilienthal, Etrich's father acquired some advanced gliders.[1]
Subsequently to a Friedrich Ahlborn paper[2] describing the flying seed of Zanonia macrocarpaha, published in 1897, Etrich along with colleague Franz Xaver Wels designed an unmanned glider of similar form and flew it successfully in 1904. Attempts to add an engine failed, but a successful manned glider was flown in 1906.[1]
He also possibly worked with the pilot Karl Illner.[1]
He moved to Vienna, where he had his second laboratory in the Wiener Prater at the Rotunde. In 1907, he built his Etrich I, the Praterspatz ("Prater park Sparrow"). The aircraft was unsuccessful. Etrich rented two hangars at Wiener-Neustadt and continued to develop the Taube ("Dove"). Incidentally, Wels visited Paris and studied the aircraft of the Wright Brothers and split with Etrich over the question of whether to build a monoplane or biplane.[1]
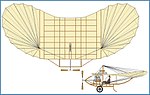
In 1910, the Etrich II, or Taube, was first flown. Etrich nearly broke his back when the Taube crashed, during one of the early flights. Karl Illner made all of Etrich's subsequent test flights. Etrich continued to refining the Taube, considering military requirements such landing capacity on freshly plowed fields.[1] (The Etrich II is often designated as the Etrich Taube.)
Soon after, he developed the Etrich III Möve.
In 1912 he founded Etrich Flieger Werke in Liebau (today Lubawka, Poland) and designed the "Luft-Limousinen", an aircraft with an enclosed cabin for the passengers.[1] >
He moved to Germany, founding Brandenburgische Flugzeugwerke, which became Hansa-Brandenburg after its sale to Camillo Castiglioni in 1914. Etrich had brought Ernst Heinkel with him from Liebau. Heinkel was his chief designer.[1] See Hansa und Brandenburgische Flugzeugwerke GmbH.
Edmund Rumpler, another aircraft designer, slightly modified the Taube's design, claiming to be the developer and refusing to pay licensing fees to Etrich. With the advent of World War I, Etrich made the design for his Taube freely available and dropped his lawsuit.[1]
After World War I, Etrich moved to Trautenau (now Trutnov) in the newly founded Czechoslovakia, and built the Sport-Taube. It was claimed to be faster with its 40 hp engine than the Czechoslovak military planes of the time. The authorities claimed he built the plane for smuggling and impounded his plane. Etrich was so disappointed that he abandoned his aeronautical projects and dedicated himself to the production of textile machinery.[1]
Etrich sometimes filed as "Igo Etrich", and is known both in aeronautic history and in patent originals under either of the designations.
His collaboration with Franz Xaver Wels had been substantial throughout, and was to continue, in general and in terms of patents filed, said patents among others being associated with the location Oberaltstadt near the above-mentioned Trautenau, Bohemia, which was at the time part of the Austro-Hungarian Empire.
The "Etrich Taube", or simply "Taube" is crucial to his role played later. It was and is also known by the names of the various later manufacturers who build versions of the type. It was the first military airplane to be mass-produced in Germany. It was very popular prior to the First World War, and was also used by the air forces of Italy and Austria-Hungary, with even the Royal Flying Corps operating at least one Taube in 1912. On November 1, 1911, Giulio Gavotti, an Italian aviator, dropped the world's first aerial bomb, or grenade, from his Taube monoplane over the Ain Zara oasis in Libya.[3] See Italo-Turkish War.
The Etrich Taube "Dove" is the monoplane type associated with much of our data on several organizations.
Airplanes created by Ignaz Etrich
- Etrich Möve (Year constructed: 1910)
- Etrich Taube (Year constructed: 1910)
Patents whose inventor or applicant is Ignaz Etrich
- Patent AT-1902-6911 (English title: Helmet facilitating respiration, Filing date: 1901-06-13)
- Patent GB-1902-8772 (English title: Device (helmet) facilitating respiration within closed spaces, Filing date: 1902-04-15)
- Patent FR-1902-321963 (English title: Fresh air breathing apparatus for personnes finding themselves in closed spaces, Filing date: 1902-04-24)
- Patent AT-1905-23465 (English title: Flying machine, Filing date: 1905-03-03)
- Patent US-1906-952316 (English title: Monoplane, Filing date: 1906-02-28)
- Patent FR-1906-363970 (English title: Airplane, Filing date: 1906-03-08)
- Patent AT-1909-IE (English title: Improvements in monoplane construction and design specifications, all in the furtherance of aerodynamics, Filing date: 1909-09-11)
- Patent FR-1910-410711 (English title: monoplane, Filing date: 1909-12-27)
- Patent GB-1910-14204 (English title: Improvements in monoplane construction and design specifications, all in the furtherance of aerodynamics, Supplementary to patent: Patent AT-1909-IE, Filing date: 1910-06-11)
- Patent US-1911-983697 (English title: Supporting-Surface for Flying-Machines, Filing date: 1910-08-12)
- Patent US-1911-983697 (English title: Supporting-Surface for Flying-Machines, Filing date: 1910-08-12)
- Patent FR-1911-421906 (English title: Improvements in monoplane construction and design specifications, all in the furtherance of aerodynamics, Supplementary to patent: Patent AT-1909-IE, Filing date: 1910-09-10)
Publications by or about Ignaz Etrich
- Beach, 1913, The Etrich monoplanes. Description of several of the latest aeroplanes of the Austrian pioneer (Simple title: The Etrich monoplanes, Journal: Scient. Amer. Suppl.)
- Supf, 1958, Das Buch der deutschen Fluggeschichte (Simple title: Book of German Flight-History)
- Keimel, 1981, Österreichs Luftfahrzeuge (Simple title: Österreichs Luftfahrzeuge)
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 Ignaz "Igo" Etrich on English Wikipedia
- ↑ "Über die Stabilität der Flugapparate", see Ahlborn, 1897, Der Schwebflug und die Fallbewegung ebener Tafeln in der Luft, Stabilität der Flugapparate
- ↑ Etrich Taube on English Wikipedia
Sources
Ignaz "Igo" Etrich on English Wikipedia, Ignaz "Igo" Etrich on French Wikipedia, Ignaz "Igo" Etrich on German Wikipedia
| Names | Ignaz Etrich; Igo Etrich |
|---|---|
| Birth date | 25 December 1879 |
| Death date | 4 February 1967 |
| Countries | AT, GB, FR |
| Locations | Horní Staré Město, Trutnov, Bohemia; Wien; Wiener-Neustadt; Salzburg |
| Occupations | pilot, aircraft designer, aircraft manufacturer |
| Tech areas | Airplane, Aerodynamics, Construction, Navigation, Monoplane, Design, Lift, Glider, Sustentation, Industry |
| Affiliations | |
| Wikidata id | Q84735 |