Difference between revisions of "Drachenflieger"
m (Text replacement - "|Affiliated concepts=" to "|Keywords=") |
(add Patent DE-1911-285986 with some explanation) |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:1910 - Schiemann p. 39 - Farmans Drachenflieger.png|thumb|"Farmans Drachenflieger" ([[Schiemann, 1910, Vogelflug und Kunstflug]], p. [https://archive.org/details/bub_gb_NKJXAAAAYAAJ/page/n43 39]). Schliemann uses ''Drachenflieger'' in contrast with ''Gleitflieger''.]] | [[File:1910 - Schiemann p. 39 - Farmans Drachenflieger.png|thumb|"Farmans Drachenflieger" ([[Schiemann, 1910, Vogelflug und Kunstflug]], p. [https://archive.org/details/bub_gb_NKJXAAAAYAAJ/page/n43 39]). Schliemann uses ''Drachenflieger'' in contrast with ''Gleitflieger''.]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Dragenflieger''', literally dragon-flyer, is a German term whose meaning evolved during the time period under study. In the golden age of airplane innovation, 1908–1910, ''Drachenflieger'' could by used synonymously with ''airplane'' (or ''aeroplane'' in the sense of a whole aircraft). | ||
[[Publication 5638, 1897, Langley's Flugmaschine]] suggests that Langley's ''Aerodrome'' fits into this category. Yet [[Patent DE-1890-59851]] (tagged with Drachenflieger, why?) concerns an LTA dirigible. Meanwhile ''Drachen'' usually means kite or glider. | [[Publication 5638, 1897, Langley's Flugmaschine]] suggests that Langley's ''Aerodrome'' fits into this category. Yet [[Patent DE-1890-59851]] (tagged with Drachenflieger, why?) concerns an LTA dirigible. Meanwhile ''Drachen'' usually means kite or glider. | ||
| − | By 1910 the standard meaning of | + | By 1910 the standard meaning of ''Drachenflieger'' was more or less "airplane", as shown in contemporary patents and dictionaries.<ref>[[Olavarría y Martínez, 1912, Diccionario téchinco-automovilista y de aeronáutica]], p. [https://babel.hathitrust.org/cgi/pt?id=uc1.$b570349;view=1up;seq=38 34].</ref> (Yet [[Patent DE-1911-285986]] describes a "Drachenflieger" with flapping, not fixed, wings.) |
| + | |||
| + | It has since come to mean "hang-glider". | ||
{{References}} | {{References}} | ||
{{Techtype | {{Techtype | ||
| + | |Enclosing categories=German tech terms | ||
|Keywords=airplane; glider | |Keywords=airplane; glider | ||
}} | }} | ||
| Line 13: | Line 18: | ||
{{Standard techtype reports}} | {{Standard techtype reports}} | ||
{{Publication keywords report|Drachenflieger}} | {{Publication keywords report|Drachenflieger}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:German]] | ||
Latest revision as of 04:26, 28 October 2022
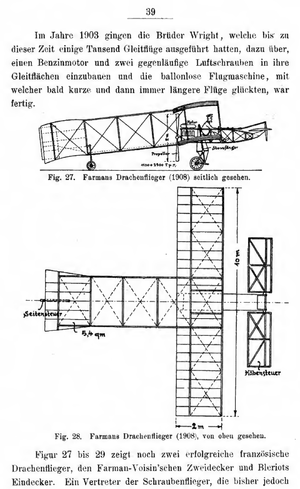
Dragenflieger, literally dragon-flyer, is a German term whose meaning evolved during the time period under study. In the golden age of airplane innovation, 1908–1910, Drachenflieger could by used synonymously with airplane (or aeroplane in the sense of a whole aircraft).
Publication 5638, 1897, Langley's Flugmaschine suggests that Langley's Aerodrome fits into this category. Yet Patent DE-1890-59851 (tagged with Drachenflieger, why?) concerns an LTA dirigible. Meanwhile Drachen usually means kite or glider.
By 1910 the standard meaning of Drachenflieger was more or less "airplane", as shown in contemporary patents and dictionaries.[1] (Yet Patent DE-1911-285986 describes a "Drachenflieger" with flapping, not fixed, wings.)
It has since come to mean "hang-glider".
References
| Enclosing categories | German tech terms |
|---|---|
| Subcategories | |
| Keywords | Airplane, Glider |
| Start year | |
| End year |
This wiki has 22 patents in category "Drachenflieger".
Patents in category Drachenflieger
- Patent DE-1891-59851 (English title: Steerable airship, Inventors: Stewart Cairncross, Supplementary to patent: Patent DE-1890-59851, Filing date: 1890-07-22)
- Patent AT-1907-30944 (English title: Drachenflieger, Inventors: William Henry Fauber, Supplementary to patent: Patent FR-1906-363017, Filing date: 1906-07-16)
- Patent AT-1908-36566 (English title: Drachenflieger, Inventors: Wilbur Wright • Orville Wright)
- Patent AT-1909-41555 (English title: Airplane, Inventors: Gustave Whitehead • Stanley Yale Beach, Supplementary to patent: Patent US-1908-881837, Filing date: 1908-03-09)
- Patent AT-1909-41978 (English title: Drachenflieger, Inventors: Thomas Malek, Filing date: 1908-06-30)
- Patent DE-1908-232250 (English title: Airplane with oscillating aerodynamic surfaces mounted on transverse axis of frame, Inventors: Alexander Baumann • Ernst Emil Freytag, Filing date: 1908-07-31)
- Patent AT-1909-41979 (English title: Airplane, Inventors: Anthony Rudolph Silverston, Filing date: 1908-09-29)
- Patent AT-1911-49251 (English title: Airplane, Inventors: Robert Esnault-Pelterie, Filing date: 1908-10-16)
- Patent AT-1910-44933 (English title: Drachenflieger, Inventors: Arthur Henry Edwards, Filing date: 1909-02-10)
- Patent CH-1909-49709 (English title: Airplane, Inventors: John Seiler, Supplementary to patent: Patent US-1908-927605, Filing date: 1909-07-20)
- Patent AT-1909-45369 (English title: Toy Airplane, Inventors: Raimund Hengl, Filing date: 1909-09-02)
- Patent AT-1909-50881 (English title: Airplane, Inventors: Anton Kreidler, Filing date: 1909-10-06)
- Patent AT-1909-48865 (English title: Airplane with arrow-shaped sustaining surface, Inventors: Max Notthaft, Filing date: 1909-12-16)
- Patent AT-1910-53705 (English title: Airplane chassis, Inventors: George Sturgess • Charlotte Sturgess, Supplementary to patent: Patent GB-1908-26924, Filing date: 1910-03-10)
- Patent LU-1910-8455 (English title: Glider-tye airplane, Inventors: Anton Gammisch, Filing date: 1910-05-09)
- Patent AT-1910-58962 (English title: Airplane with aerodynamic surfaces mounted on the frame around the transverse axis, Inventors: Emil Freytag • Alexander Baumann, Supplementary to patent: Patent DE-1908-232250, Filing date: 1910-05-30)
- Patent AT-1910-50757 (English title: Airplane, Inventors: Hugo Zalaudek, Filing date: 1910-06-07)
- Patent DE-1910-248876 (English title: Motorized airship with detachable gondola, Inventors: Emil Wedekind, Filing date: 1910-11-20)
- Patent DE-1911-285986 (English title: Aircraft with flapping wings, Inventors: Richard Mentz, Filing date: 1911-08-22)
- Patent AT-1912-62542 (English title: Airplane, Inventors: Alois Krischke, Filing date: 1912-07-09)
- Patent AT-1913-66537 (English title: Airplane, Inventors: Max Müller, Filing date: 1913-05-17)
- Patent DE-1915-301930 (English title: Aircraft, Inventors: Richard Mentz, Supplementary to patent: Patent DE-1911-285986, Filing date: 1915-08-20)
Publications referring to Drachenflieger
- Kress, 1896, Drachenflieger und Schraubenflieger (Simple title: Airplanes and helicopters, Journal: Zeitschr. Luftsch.)
- Kress, 1896, Ueber die Stabilität des Drachenfliegers in ruhiger und bewegter Luft (Simple title: About the stability of the Drachenflieger in calm and moving air, Journal: Zeitschr. Luftsch.)
- Publication 5638, 1897, Langley's Flugmaschine (Simple title: Langley's flying machine, Journal: Ill. Aër. Mitt.)
- Platte, 1898, Neue Ideen (Simple title: New ideas, Journal: Ill. Aër. Mitt.)
- Wellner, 1901, Werth und Bedeutung der Radflieger für die Luftschiffahrt (Simple title: Value and importance of the Radflieger for aeronautics, Journal: Ill. Aër. Mitt.)
- Hoernes, 1903, Die Luftschiffahrt der Gegenwart (Simple title: The airship of the present)
- Publication 2706, 1903, Octave Chanute in Wien (Simple title: Octave Chanute in Wien, Journal: Wien. Luftsch. Zeit.)
- Publication 13002, 1906, Die Wriqht-Frage (Simple title: The Wriqht question, Journal: Wien. Luftsch. Zeit.)
- Hofman, 1907, Mein Drachenflieger (Simple title: My Drachenflieger, Journal: Ill. Aër. Mitt.)
- Kress, 1907, Aeronautische Terminologie (Simple title: Aeronautical terminology, Journal: Ill. Aër. Mitt.)
- Wellner, 1908, Ueber Luftschrauben und Schraubenflieger (Simple title: About propellers and helicopters, Journal: Ill. Aër. Mitt.)
- Hans Dominik, F. M. Feldhaus, Otto Neuschler, A. Stolberg, O. Steffens, Hugo Eckener, N. Stern, 1909, Die Eroberung der Luft (Simple title: The Conquest of the the Air, Journal: Union deutsche Verlaggesellschaft • Wien. Luftsch. Zeit.)
- Dienstbach, 1909, Die neuesten Arbeiten der amerikanischen 'Aerial Experiment Association' (Simple title: The latest works of the American 'Aerial Experiment Association', Journal: Ill. Aër. Mitt.)
- Schiemann, 1910, Vogelflug und Kunstflug (Simple title: Bird flight and artificial flight)
Publications referring to Drachenflieger
- Kress, 1896, Drachenflieger und Schraubenflieger (Simple title: Airplanes and helicopters, Journal: Zeitschr. Luftsch.)
- Kress, 1896, Ueber die Stabilität des Drachenfliegers in ruhiger und bewegter Luft (Simple title: About the stability of the Drachenflieger in calm and moving air, Journal: Zeitschr. Luftsch.)
- Publication 5638, 1897, Langley's Flugmaschine (Simple title: Langley's flying machine, Journal: Ill. Aër. Mitt.)
- Platte, 1898, Neue Ideen (Simple title: New ideas, Journal: Ill. Aër. Mitt.)
- Wellner, 1901, Werth und Bedeutung der Radflieger für die Luftschiffahrt (Simple title: Value and importance of the Radflieger for aeronautics, Journal: Ill. Aër. Mitt.)
- Hoernes, 1903, Die Luftschiffahrt der Gegenwart (Simple title: The airship of the present)
- Publication 2706, 1903, Octave Chanute in Wien (Simple title: Octave Chanute in Wien, Journal: Wien. Luftsch. Zeit.)
- Publication 13002, 1906, Die Wriqht-Frage (Simple title: The Wriqht question, Journal: Wien. Luftsch. Zeit.)
- Hofman, 1907, Mein Drachenflieger (Simple title: My Drachenflieger, Journal: Ill. Aër. Mitt.)
- Kress, 1907, Aeronautische Terminologie (Simple title: Aeronautical terminology, Journal: Ill. Aër. Mitt.)
- Wellner, 1908, Ueber Luftschrauben und Schraubenflieger (Simple title: About propellers and helicopters, Journal: Ill. Aër. Mitt.)
- Hans Dominik, F. M. Feldhaus, Otto Neuschler, A. Stolberg, O. Steffens, Hugo Eckener, N. Stern, 1909, Die Eroberung der Luft (Simple title: The Conquest of the the Air, Journal: Union deutsche Verlaggesellschaft • Wien. Luftsch. Zeit.)
- Dienstbach, 1909, Die neuesten Arbeiten der amerikanischen 'Aerial Experiment Association' (Simple title: The latest works of the American 'Aerial Experiment Association', Journal: Ill. Aër. Mitt.)
- Schiemann, 1910, Vogelflug und Kunstflug (Simple title: Bird flight and artificial flight)